
The care economy comprises the vast, often invisible, network of unpaid work such as caregiving, education, and domestic chores that underpins societies worldwide. Despite being essential for the well-being and functioning of individuals and communities, this labor is frequently undervalued and overlooked in traditional economic calculations. As populations age and social needs evolve, the significance of care work—performed predominantly by women—will only grow in the future economy. Recognizing and investing in the care economy not only promotes gender equality but also fosters sustainable development and social cohesion. Properly valuing unpaid care work through policy measures, social protection, and economic incentives is vital for building resilient, inclusive societies. In the future, integrating the care economy into mainstream economic frameworks will be crucial for achieving both economic prosperity and social well-being.
- Učiteľ: Chiara Landikusic
- Učiteľ: Elaya Nur Rasimgil
- Učiteľ: Kamil Piotr Sulich
- Učiteľ: Alisa Yurtaieva

Consumer psychology in Economy 5.0 is characterized by increasingly data-driven and personalized decision-making processes. With advanced digital environments, consumers are exposed to tailored advertisements and recommendations that match their preferences, needs, and behaviors. AI-powered platforms analyze user data in real time, creating highly individualized shopping experiences. As a result, purchasing decisions are influenced not only by product features but also by emotional engagement and perceived relevance. Social proof, such as reviews and influencer endorsements, plays a larger role in shaping choices. Additionally, the convenience of digital payments and seamless online-to-offline integration shortens the decision-making cycle. Consumers expect transparency, ethical practices, and instant gratification, further altering traditional buying patterns. In summary, digital personalization and environment are fundamentally transforming how consumers decide what, when, and how to purchase in Economy 5.0.
- Učiteľ: Anastasiia Fatkullina
- Učiteľ: Agnieszka Jaworsko
- Učiteľ: Marta Szumlinska
- Učiteľ: Kajetan Zbarachewicz
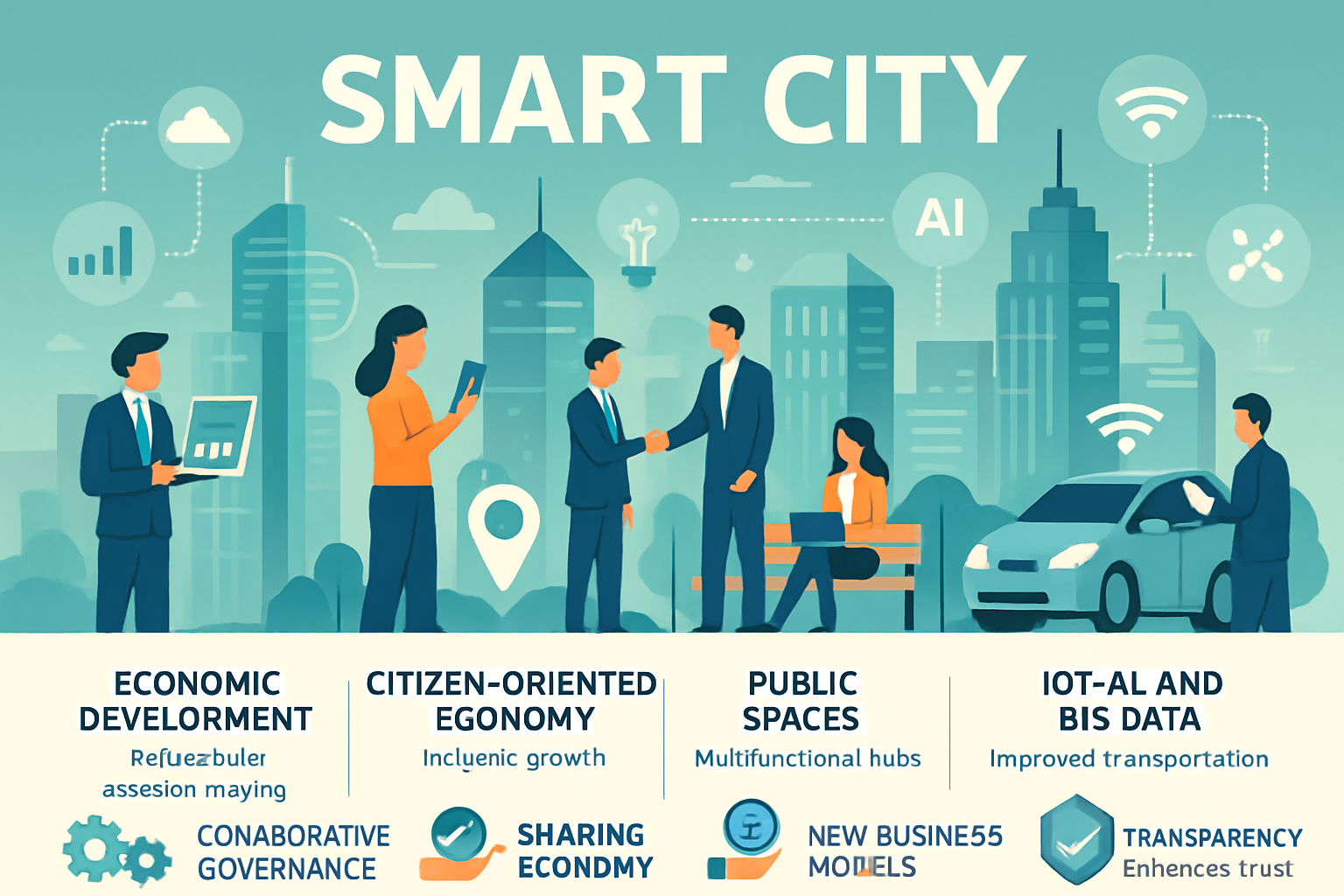
Cities of the future will be shaped by smart technologies that integrate digital infrastructure with urban planning, fostering efficient and sustainable environments. Economic development in these cities relies on data-driven decision-making, optimizing resource allocation and reducing operational costs. The citizen-oriented economy prioritizes inclusive growth, enabling residents to participate in and benefit from digital platforms and services. Public spaces are transformed into multifunctional hubs that encourage social interaction, innovation, and entrepreneurship. Smart cities leverage IoT, AI, and big data to improve transportation, energy use, and public safety. These advancements attract investment, stimulate job creation, and support new business models such as the sharing economy. Collaborative governance empowers citizens, making urban development more responsive to community needs. Technology-driven transparency enhances trust and accountability in public administration. The integration of economy, technology, and public space generates adaptive, resilient urban ecosystems. Ultimately, cities of the future strive to balance economic growth with social well-being and environmental sustainability.
- Učiteľ: Joanna Jezowska
- Učiteľ: Aleksander Michalowski
- Učiteľ: Oliver Nenadic
- Učiteľ: Stella Salov

Digital equality means ensuring everyone has equal access to digital technologies, internet connectivity, and digital skills. To prevent a new form of social exclusion, it is crucial to address the digital divide by expanding affordable broadband and device access in underserved communities. Governments and private sectors should invest in digital infrastructure, especially in rural and low-income areas. Providing digital literacy education helps people of all ages confidently use technology. Inclusive design in digital platforms ensures accessibility for people with disabilities. Public spaces like libraries should offer free internet and digital resources. Policies must target marginalized groups, such as the elderly or minorities, to close participation gaps. Partnerships with NGOs and community organizations can deliver tailored support. Continuous monitoring of digital inclusion efforts ensures no one is left behind. Ultimately, digital equality empowers social participation, economic growth, and civic engagement for all.

In Economy 5.0, the future of work will be characterized by the emergence of new professions that integrate advanced technologies with human-centric values. Roles such as AI ethicists, digital sustainability consultants, human-machine collaboration specialists, and data trust officers will become increasingly important. The job market will demand skills in artificial intelligence, data analytics, digital literacy, emotional intelligence, creativity, and adaptability. Lifelong learning and interdisciplinary knowledge will be essential, as workers will need to continuously upskill to keep pace with technological change. Soft skills—such as critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving—will complement technical expertise. To prepare for this evolving landscape, individuals and organizations should invest in continuous education, embrace flexible learning pathways, and foster a culture of innovation and resilience.
- Učiteľ: Grzegorz Czarnomysy
- Učiteľ: Kateryna Deinega
- Učiteľ: Marek Kostur
- Učiteľ: Marian Kovac
- Učiteľ: Ian Milisa
- Učiteľ: Jana Rakus Gasperova
- Učiteľ: Katarina Svejnova Hoesova
- Učiteľ: Lara Taslak

Sustainability is the foundation of Economy 5.0, which connects economic growth with environmental protection. Modern economic development should no longer be at the expense of the planet – profit and protecting the environment do not have to be opposites. On the contrary, ESG principles (environmental, social, and governance standards) are becoming key criteria for investments and business strategies. The circular economy supports efficient use of resources, waste reduction, and reuse of materials, which brings new opportunities for growth and innovation. Green innovations help create products and services that lower environmental burdens and open new markets. Economy 5.0 emphasizes that long-term prosperity is only possible when profit and care for the planet go hand in hand, ensuring a sustainable future for the next generations.
- Učiteľ: Gabrijel Livoic
- Učiteľ: Lara Matusko
- Učiteľ: Bruna Miscevic
- Učiteľ: Katarina Tonsic
- Učiteľ: Wenlong Zheng
This course offers a comprehensive exploration of the platform economy and China's dynamic Internet platform development. It combines theoretical knowledge with real-world examples, delving into key concepts such as network effects, the chicken-and-egg paradox, and Internet governance and operations. By the end of the course, students will be able to analyze platform businesses, understand their economic mechanisms, and formulate strategic decisions in the platform context.
- Učiteľ: Yazhao Lyu
|
Learning outcomes of the course: It is a Chinese learning and teaching course, which aims to enable the local students to acquire basic Chinese linguistic competence as well as the visiting Chinese students to practice their Chinese teaching skills in the international context. Therefore, the teacher is really a facilitator in the course: he is going to build a platform throughout the course to facilitate: on the one hand, local students to learn Chinese from visiting Chinese students and teacher; on the other hand, Chinese students to practice their “teaching Chinese as a foreign language” skills in the real international setting. And the final evaluation will be based on: for Chinese students, how well they have practiced their language teaching skills and the effect of their teaching—how well the local students have acquired the linguistic competence prescribed in the course goal—the latter is also the major evaluation indicator for the local students (through oral tests, group conversations or demonstration activities). |
- Učiteľ: RunZhu Xiong

Through the study of this course, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of new media marketing theories and practices, and be able to apply this knowledge to actual e -commerce operations. They will become familiar with the characteristics and development trends of new media, as well as mainstream new media platforms and their marketing tools. Students will be able to design appropriate marketing strategies for products according to the rules of different platforms, helping enterprises achieve their marketing goals. This course aims to cultivate students' market analysis and strategy - making abilities, enhance their innovative thinking and creative expression capabilities, encourage students to develop their ability to use new tools and skills, especially the ability to apply general - purpose artificial intelligence technology, and develop their teamwork and project management skills. As a result, students will be able to successfully face various challenges and seize development opportunities in the field of new media marketing.
- Učiteľ: Haiyuan Hu
- Učiteľ: Marcel Lincenyi
“Cultural Heritage in Jiangnan (Regions South of the Yangtze River)” offers an in-depth exploration of the cultural heritage of the Jiangnan region in China, covering both tangible and intangible aspects. Through the study of this course, students will develop a comprehensive understanding of the cultural heritage of Jiangnan, including its historical significance, artistic value, and cultural appeal. They will learn to present, analyze, and critically discuss the unique features of Jiangnan’s cultural heritage and gain insights into traditional cultures by comparing and contrasting those of their home countries and China. They will cultivate the ability to critically engage with cultural and heritage-related topics, fostering a deeper appreciation for cultural diversity. And they will also develop a scientific perspective on world heritage conservation, emphasizing the importance of preserving cultural heritage for future generations. By the end of the course, students will not only have a profound appreciation for the poetic charm and rich cultural allure of Jiangnan but will also have enhanced their cross-cultural competence, preparing them to engage meaningfully with diverse cultural contexts.
- Učiteľ: Ming Li
- Učiteľ: International Department
- Učiteľ: Marek Kostur
- Učiteľ: Marian Kovac
- Učiteľ: Jana Rakus Gasperova
- Učiteľ: George Sibichen
- Učiteľ: Katarina Svejnova Hoesova
